Cultural, historical, adventure, and custom customized trips are just a few of the tours that Deluxe trips offer in Egypt and Jordan.
The Old Kingdom: (c. 2686–2181 BCE), or "Age of the Pyramids," solidified Egypt's centralized state and the massive building. Marked by powerful pharaohs, the period saw the construction of the massive pyramids at Giza and the Sphinx, across divine kingship. Religion, art, and engineering were more advanced than previously, testing Egypt's early success at state making and cultural identity.
Middle Kingdom: (c. 2055–1650 BCE) was a period of domestic peace and cultural rebirth. It was famous for literary and artistic sophistication with emphasis on centralization, justice, and reform. Pharaohs revived connection with the people through emphasis on irrigation, agriculture, and extension of trade networks, stabilizing the economy and culture of Egypt.
New Kingdom: The New Kingdom (c. 1550–1070 BCE) was Egypt's imperial heyday, an age of expansion by the military, great pharaohs like Ramses II and Tutankhamun, and tremendous temple monuments. Egypt was a world power, accumulating vast riches, world power, and unparalleled craftsmanship.
The focal aspect of Egyptian existence in the ancient world is the symbolic hieroglyphic script. Not a system of writing at all, these stunning symbols were meaningful in terms of religion, bureaucracies, and art. Carved on ancient tombs, Egyptian artifacts, and temple walls like Karnak Temple, hieroglyphics documented gods, kings, and astronomical events.
Scribes were most esteemed, preserving the cultural and religious heritage of ancient Egypt in scrolls and carvings. The actions and beliefs of Egypt's pharaohs were recorded in hieroglyphics to live eternally.
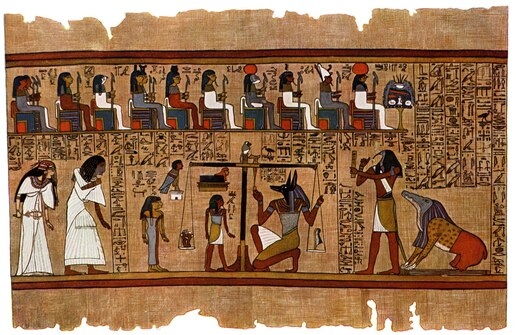
At the center of Egyptian spirituality and art was the exceedingly complex process of mummification, the role of which was to prepare the dead for the afterlife. The complex ritual testified to extensive concern for the journey of the soul, one that begins in ancient Egypt religion and culture.
In Egypt's Valley of the Kings, pharaohs' graveyard, mummies were covered in elaborate coffins along with Egyptian riches symbolizing protection and prosperity. Preservation of the body was carried out cautiously on the assumption of being resurrected by God—a cornerstone of ancient Egyptian society.
At the center of Egyptian spirituality and art was the exceedingly complex process of mummification, the role of which was to prepare the dead for the afterlife. The complex ritual testified to extensive concern for the journey of the soul, one that begins in ancient Egypt religion and culture.
In Egypt's Valley of the Kings, pharaohs' graveyard, mummies were covered in elaborate coffins along with Egyptian riches symbolizing protection and prosperity. Preservation of the body was carried out cautiously on the assumption of being resurrected by God—a cornerstone of ancient Egyptian society.
Luxor, the Thebes of the Old Kingdom capital, has the distinction of possessing two of Egypt's greatest religious monuments: the Temple of Karnak and the Temple of Luxor. Temple of Luxor represents the pinnacle of ancient Egyptian culture, combining colossal stone architecture, beautifully carved architectural ornaments, and enormous ceremonial spaces into endlessly acted-out rituals of divine worship. A walk at Luxor is a step into the past with each column and wall narrating the pharaohs', priests', and astral rituals' tales chiseled out of the past.
Karnak Temple, the largest religious structure ever constructed on this earth, dazzles people with sky-piercing obelisks, colossal statues, and enormous courtyards edged by rows of giant pillars. Constructed for the Theban triad Amun, Mut, and Khonsu, it was enlarged by pharaohs over a period of hundreds of years to appease the gods. These temples are not just sites of history—but also of what effectively amounts to sacred ground where ancient art, engineering, and religious ardor all converge in overwhelming synergy.
Egyptian artifacts found in ancient graves contain distinctive details about daily life, royal tradition, and religious beliefs of ancient Egypt. From burial masks in gold and ritualistic vessels to symbolic jewelry and statues given to gods, each object was not just a symbol but played a purpose in crossing into the afterlife. This funeral wealth was planned to some extent to protect and guide the soul, evidence of Egypt's deep reverence for death, divinity, and immortality. Hieroglyphic writing and elaborate carving on these items are medium of advanced myth and world order and turn each relic into a glimpse into the thinking and faith of a lost and ancient civilization.
Many objects, such as the canopic jars used in mummification, demonstrate how science and magic were so intertwined with one another in Egyptian death lore. Because Egypt's arid conditions and safe storage in tombs preserved many of these, thousands of objects like them have survived for millennia. Today they still glitter with the splendor and luxury of one of the world's most fascinating old civilizations.
Egypt's pharaohs were not only rulers—but divine mediators of the gods and mortals, influencing ancient Egypt's history for over three thousand years. From the builders of the pyramids of the Old Kingdom like Khufu and Djoser, through war kings of the New Kingdom like Ramses II and Thutmose III, each pharaoh has left his own record etched in hieroglyphics, old tombs, and colossal temples like the Karnak Temple and Luxor temples. Adored as gods in life, they oversaw the mummification process, ordered stunning ancient Egyptian frescoes, and lined the Valley of the Kings with richly decorated tomb chambers. Their reigns were to become the embodiment of the very best of Egyptian civilization, the marriage of power and divinity and engineering in a civilization that fascinates the world today.
Ancient Egyptian society was firmly anchored in multi-layered religious cosmology built on gods like Ra (sun god), Osiris (dead god), and Isis (fertility goddess and magician). Mythological myths of mythological magnitudes dominated politics to mundane rituals that governed everyday life. Temples and tomb chambers brimmed with hyperbolic hieroglyphics, sacrifice, and depictions of supernatural mythologies as a means to appease and align oneself with gods. Funerary rituals such as mummification showed their belief in the reality of an afterlife, preserving the body being the ultimate step of keeping the soul alive for all time.
Egyptians practiced in religious festivities, built monumental temples, and created mysterious symbolic paintings fitting for their values and cosmic order. Egyptians' culture was best comprised of identity and religion, propagated over centuries by tradition, myth, and deep respect for gods who governed earthly existence and immortality.
The magnificence of Egyptian history is exposed through the grandeur of its pharaohs, divine rituals, and eternal monuments. The Old Kingdom's pyramids to the New Kingdom's temples, every era enriched the culture of Egyptian society. The services of the gods are shown in the Luxor temples and the Karnak Temple, while the Valley of the Kings boasts richly ornamented ancient tombs where the mummification ritual offered an entry to eternal life.
By stone-carved hieroglyphics and unperturbed Egyptian artifacts, syncretism of Egyptian religion and culture continues to exist. Aestheticity in art, richness of symbols, and religiosity defined this ancient society–its legacy kept alive by ancient Egyptian painting, sacral mortuary rituals, and a variety of stories recited.
Discover now our answers to the most common questions that may come to your mind about tourism and trips to Egypt
Cultural, historical, adventure, and custom customized trips are just a few of the tours that Deluxe trips offer in Egypt and Jordan.
The Dead Sea, Petra in Jordan, the Pyramids of Giza, Luxor's historic temples, and many other famous sites can be expected to be explored with Deluxe Tours.
offer a hassle-free holiday, Deluxe Tours' packages generally include lodging, transport, meals, guided tours with experienced local experts, and entry fees to attractions.
Spring (March to May) and fall (September to November) offer the finest weather for sightseeing and outdoor activities, making those months the best times to visit Egypt and Jordan.
These two countries are close by, only a 1.5-hour flight apart, and when combined, offer a variety of distinctive experiences. We advise you to spend at least 12 days visiting both countries for a truly unforgettable experience
Combining the eclipse viewing with visits to historic sites like the Pyramids of Giza, the Valley of the Kings, and a Nile River cruise are highly recommended.
